Code Documentation
Outline
Typical workflow
This package contains a few function to draw geometric object or textures over another texture contained in a
SpriteRenderer.
The workflow of GeomDraw typically consists in the following steps:
- Create an object of the class
Drawer, associating it with theSpriteRendererover which you want to draw - Create a geometric object (or a texture) belonging to the
IDrawableclass - Use the
Drawerobject to draw theIDrawable - Save the texture as png.
// We imagine that the script is attached to the gameObject containing the SpriteRenderer
SpriteRenderer spriteRenderer = GetComponent<SpriteRenderer>()
// Creating the Drawer object
Drawer drawer = new Drawer(spriteRenderer)
// Creating a new black empty sprite in the SpriteRenderer. Size 4x4 and 100 pixels per unit
drawer.NewEmptySprite(4, 4, 100, Color.black)
// Creating a white pentagon
Vector2 center = new Vector2(2, 2);
Vector2 scale = new Vector2(2, 2);
PolygonRegular pentagon = new PolygonRegular(5, center, scale, Color.white)
// Using the Drawer object to draw
drawer.Draw(pentagon)
// Saving the image as png in the default project folder SaveImages
drawer.SavePng("pentagon")
Output
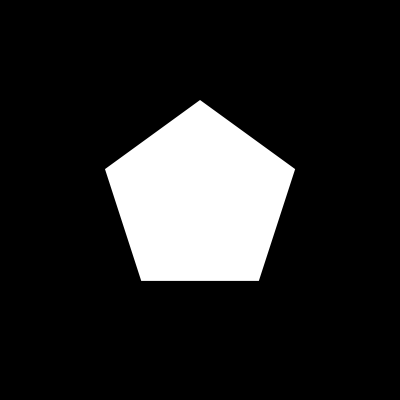
Drawer
Constructor
The Drawer class allows you to draw over the texture attached to a SpriteRenderer, which has to be specified through the contructors.
public Drawer(SpriteRenderer spriteRenderer)
Create an empty sprite
The function NewEmptySprite substitutes the current texture of the SpriteRenderer (or creates a new one if empty) with a new mono-color texture of given size and pixels per units.
public void NewEmptySprite(
float width,
float height,
float pixelsPerUnity,
Color backgroundColor
)
width and height are in world units, pixelsPerUnity is the factor epressing the number of pixels per world unit, backgroundColor sets the color.
Draw
The main function Draw edits the texture of the SpriteRenderer drawing on it a geometric element or a texture.
These elements are istances of IDrawable and can be created as discussed below.
public void Draw(IDrawable drawable, bool updateUndoer = true)
updateUndoer flags if the class Undoer should be updated with this operation. This allows to undo the last drawable but it slows down the drawing.
Bucket tool
The bucket tool colors all the neighbours pixels of a point having a “similar” color of the pixel at that point.
public void Bucket(Vector2 point, Color color, float sensitivity)
The point has coordinates in world units, and the origin is the bottom left corner of the texture. sensitivity is the parameter that sets how much similar is the neighbouring color to be considered as a neighbours. It is normalized between 0 and 1. Check out the bucket tool example.
Saving
To save the texture on the attached SpriteRenderer as png, one can call the following functions. In the function name the “.png” is not required.
// Save the image in the default directory SaveImages
public void SavePng(string name)
// Save the image in a choosed directory
public void SavePng(string name, string dirPath)
Drawable elements
Transformations
All the drawable elements share a series of common functions that allows them to be geometrically transformed. Check out the transformation example.
The translation moves the drawable of an amount and direction specified by the vector in the argument (in world units).
public void Translate(Vector2 translation)
This rotates the drawable of an angle in radiants with respect to a rotational center.
If isRelative the rotational center is relative to the center of the rectangle that contains the
drawable, otherwise the rotational center is in world coordinates, with the origin as the bottom left
corner of the modified texture.
public void Rotate(float radAngle, Vector2 rotCenter, bool isRelative)
Reflection of the drawable with respect to the x or y axis (Axis is an enumerator that can be
Axis.x or Axis.y).
coord specifies the y or x coordinate of the reflection axis.
As for the rotation, isRelative sets if this coordinate is relative to the rectangle containing
the drawable or the texture coordinates.
public void Reflect(Axis axis, float coord = 0, bool isRelative = true)
Deformation of the drawable along the axis of a given factor.
coord specifies the y or x coordinate of the deformation axis, which is the line that
does not change position during the deformation.
isRelative sets if this coordinate is relative to the rectangle containing
the drawable or the texture coordinates.
public bool Deform(Axis axis, float factor, float coord = 0, bool isRelative = true)
Lines
There are two types of lines: the broken lines and the Bezier curves, shown below.
Their style can be specified by the following class that allows you to choose the line
thickness in world units and its color.
public LineStyle(float thickness, Color color)
Broken line
A broken line connects a list of points with segments. The points coordinates are in world units with the origin on the left bottom corner of the texture.
Specitying isClosed the last and the first points will be connected.
public BrokenLine(Vector2[] points, bool isClosed, LineStyle style)
// Constructor with black line
public BrokenLine(Vector2[] points, bool isClosed, float thickness)
Bezier curve
GeomDraw draws quadratic and cubic Bezier curves (wiki). All the constructors use the convention that the first and the last points are the two points connected by the curve, the intermediate points (one for the quadratic and two for the cubic) are the control points defining the curvature.
// Quadratic Bezier curve, starting from p1, ending in p3
public BezierCurve(Vector2 p1, Vector2 p2, Vector2 p3, LineStyle style)
// black line
public BezierCurve(Vector2 p1, Vector2 p2, Vector2 p3, float thickness)
// Cubic Bezier curve, starting from p1, ending in p4
public BezierCurve(Vector2 p1, Vector2 p2, Vector2 p3, Vector2 p4, LineStyle style)
// black line
public BezierCurve(Vector2 p1, Vector2 p2, Vector2 p3, Vector2 p4, float thickness)
Quadratic and cubic Bezier curves, together with broken lines are shown in an example.
Shapes
Circle
A circle given the center the radius (world units, origin of the texture).
The border style is set by a LineStyle object which has 0 thickness by default.
public Circle(
Vector2 center,
float radius,
olor color,
LineStyle borderStyle = new LineStyle()
)
Circular sector
The circular sector is an arc of a circle defined between two angles in radiants.
The border style is set by a LineStyle object which has 0 thickness by default.
public CircularSector(
Vector2 center,
float radius,
float angle1,
float angle2,
Color color,
LineStyle borderStyle
)
Ellipse
An ellipse given the two semi axis values, center and rotation angle in radiants.
The border style is set by a LineStyle object which has 0 thickness by default.
public Ellipse(
Vector2 center,
float semiAxisX,
float semiAxisY,
float rotationAngle,
Color color,
LineStyle borderStyle = new LineStyle()
)
// No rotation
public Ellipse(
Vector2 center,
float semiAxisX,
float semiAxisY,
Color color,
LineStyle borderStyle = new LineStyle()
)
Ellipse sector
Ellipse sector between two angles in radiants.
The border style is set by a LineStyle object which has 0 thickness by default.
public EllipseSector(Vector2 center,
float semiAxisX,
float semiAxisY,
float startAngle,
float endAngle,
float rotationDegAngle,
Color color,
LineStyle borderStyle = new LineStyle()
)
Polyigon
A polygon is the closed shape delimited by the segments joining the points specified as argument.
The code check if there are self intersections of the segments. In that case the polygon becomes the
external path of segments.
This has been also demonstrated in an example.
The border style is set by a LineStyle object which has 0 thickness by default.
public Polygon(
Vector2[] vertices,
Color color,
LineStyle lineStyle = new LineStyle()
)
Regular polygon
A polygon inscribed in an ellipses whose axis define the scale. The nVertices are on the perimeter of the ellipses
at equally spaced angles. The first corner is always at the top of the ellipses.
Note that if the scale values are the same this is a regular polygon.
The border style is set by a LineStyle object which has 0 thickness by default.
public PolygonRegular(
int nVertices,
Vector2 center,
Vector2 scale,
float rotation,
Color color,
LineStyle lineStyle = new LineStyle()
)
// No rotation
public PolygonRegular(
int nVertices,
Vector2 center,
Vector2 scale,
Color color,
LineStyle lineStyle = new LineStyle()
)
// A square
public Quad(
Vector2 center,
float side,
float rotation,
Color color,
LineStyle borderStyle = new LineStyle()
)
Composite shape
Shape delimited by the lines in argument, that can be BrokenLine or a BezierLine. Those lines have to be in clockwise order.
If two cnsecutive lines don’t have the final point coinciding with the initial point of the next, will be joined with a straight
segment.
The function handles the self intersections as the Polygon.
The border style is set by a LineStyle object which has 0 thickness by default.
public CompositeShape(
IDrawableLine[] lines,
Color color,
LineStyle lineStyle = new LineStyle()
)
Check out the composite shape example.
Textures
Textures can be merged one on the top of each other. To this end the foreground texture must become a DrawableTexture object.
// To build the texture you need the 1-dim array containing all the pixel colors,
// the number of pixels on the width, the origin coordinates with respect the origin
// of the background texture and the number of pixels per unit
public DrawableTexture(Color[] pixels, int nPixelsX, Vector2 origin, float pixelPerUnit)
// Contruction using the Unity Texture2D. The first mip level will be considered
public DrawableTexture(Texture2D texture, Vector2 origin, float pixelPerUnit)
// Construction through the Unity Sprite
public DrawableTexture(Sprite sprite, Vector2 origin)
The drawing procedure is exactly as the drawing of the geometrical shapes thorugh the Drawer class. Note that also textures can be transformed as discussed before.
See the texture example and a possible application of this function to
randomly spawn objects on a single texture.
Undoer
It undos the last drawing. It works only if the drawing has been drawn with the option updateUndoer.
In that case a new component Undoer is created on the same gameObject of the SpriteRenderer and can be called for the undo.
For an example see the bucket tool example.
// Function of the class Undoer that launch the undo
public void Undo()